Steatosis Hepatis Grad 2
Steatosis hepatis grad 2. It is projected to become a leading indication for liver transplantation superseding hepatitis C. Fatty liver disease FLD also known as hepatic steatosis is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Dieser medizinische Begriff wurde für Sie übersetzt von Evi Friedrich Ärztin Dresden.
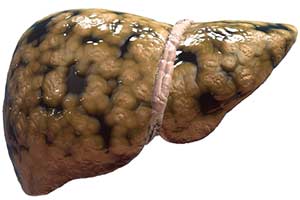
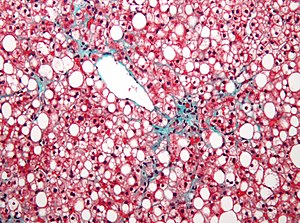
In histological terms this usually appears as macrovacuolar steatosis with large intracytoplasmic vacuoles displacing the nucleus to the periphery of the cells. Liver steatosis is graded based on the percentage of fat within the hepatocytes. Grade 1 074 and 081.
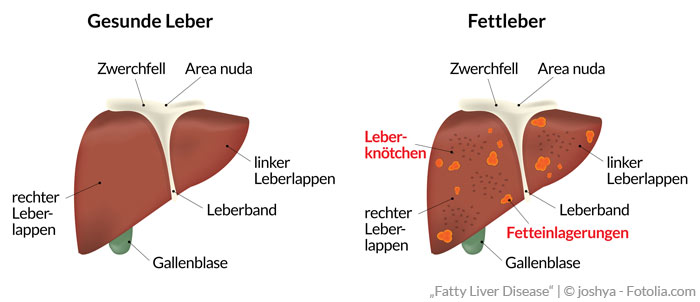
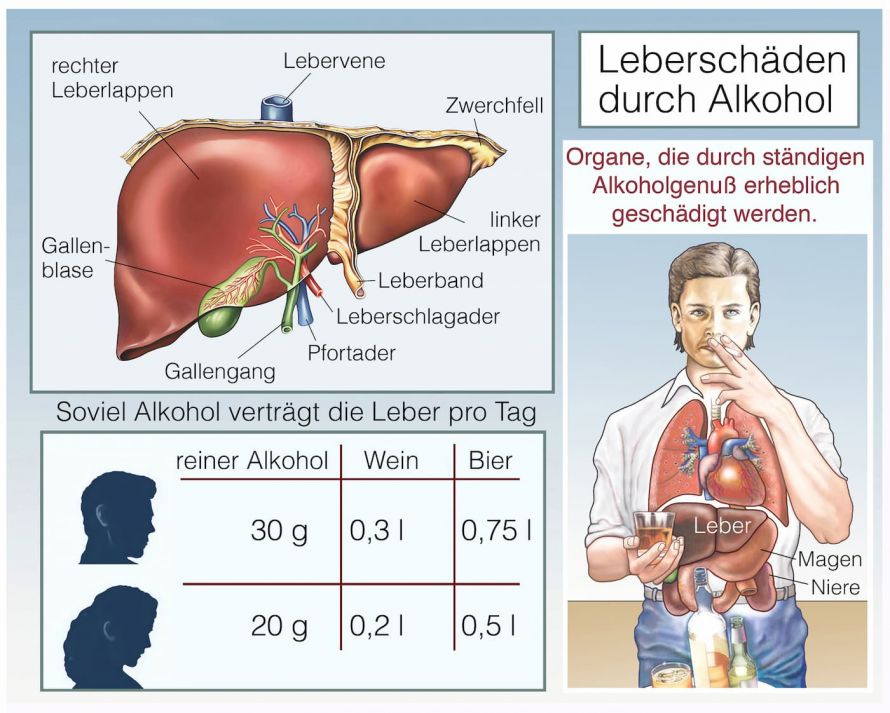
Dabei ist in weniger als zwei Drittel der Leberzellen vermehrt Fett eingelagert. 3 Simple hepatic steatosis is a. Causes of fatty liver.
A multi-center retrospective cohort study. Rata aparitiei carcinomului hepatocelular este similara cu alte suferinte hepatice cronice 2. Hepatic steatosis is becoming the most common cause of chronic liver disease and also contributes to worsening Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
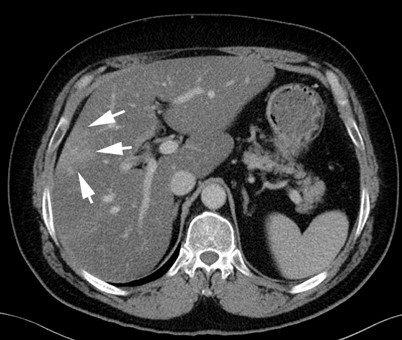
Diffusely increased hepatic echogenicity but periportal and diaphragmatic echogenicity is still appreciable. Steatoza hepatica poate fi intalnita la examenul histopatologic in urmatoarele conditii. In case of grade 1 G1 hepato-steatosis patients Resistance index RI ranges from 076-085 mean.
Diffusely increased hepatic echogenicity obscuring periportal echogenicity but diaphragmatic echogenicity is still appreciable. Hepatic steatosis is an accumulation of fat in the liver. However excess intrahepatic fat content is a risk factor for disease progression.
The diagnosis of hepatic steatosis. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve AUC-ROCs for ATT and PAC as a function of the steatosis grade were as follows.
However excess intrahepatic fat content is a risk factor for disease progression.
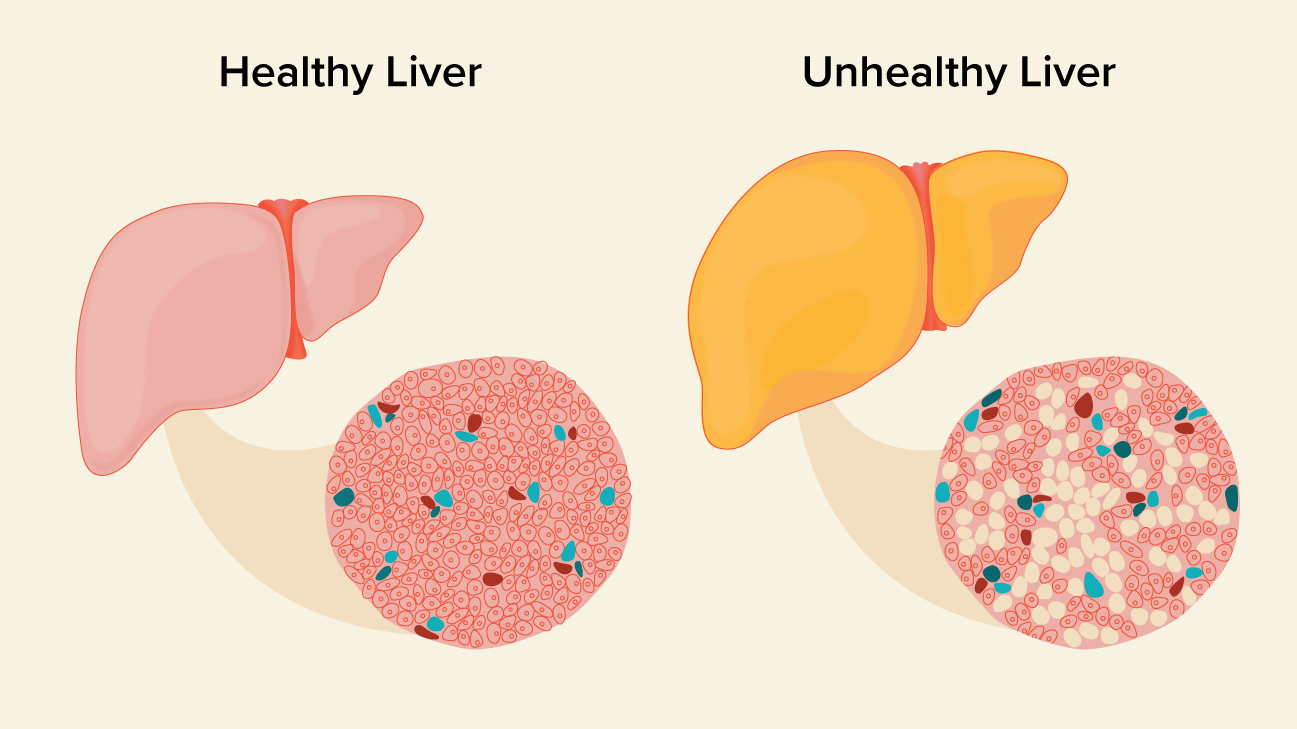
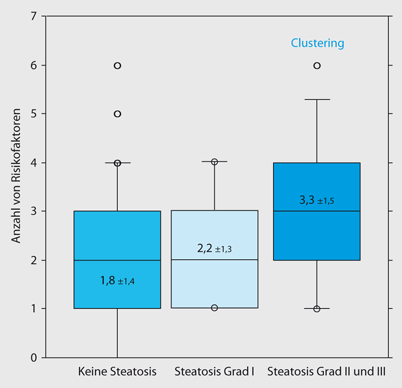
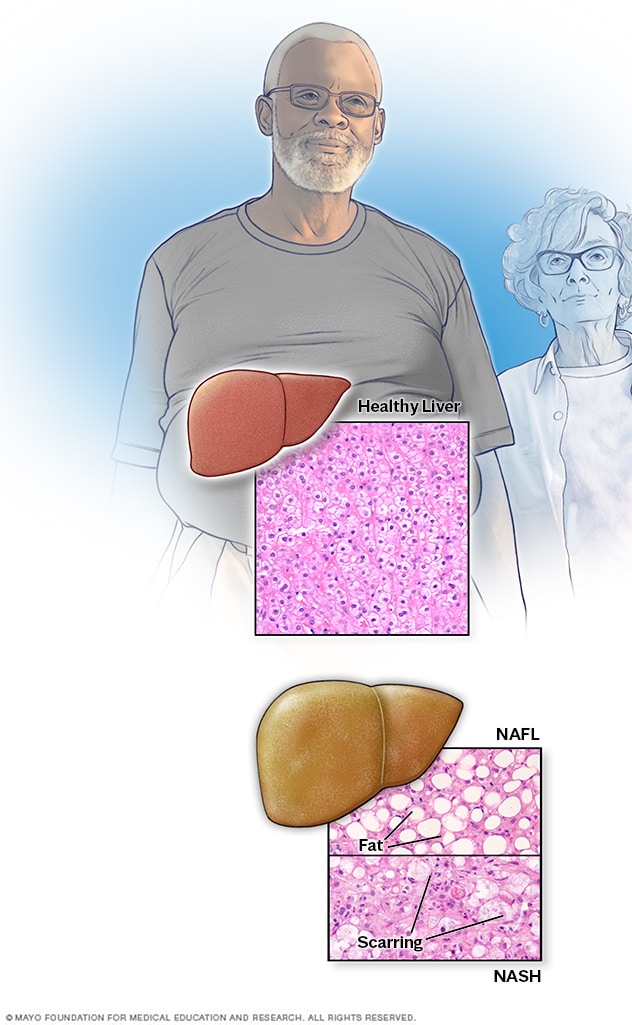
Moreover in most cases we have a mild hepatic steatosis which is medically referred to as grade 1 or 2 hepatic steatoses which usually does not lead to complications or progress to more severe stages or cause symptoms. Diffusely increased hepatic echogenicity but periportal and diaphragmatic echogenicity is still appreciable. Grade 2 080 and 085. Nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD is the most common cause of chronic liver disease in the Western world. 3 Simple hepatic steatosis is a. Verursacht wird die Leberverfettung meist durch chronischen Alkoholmissbrauch Fehlernährung oder die Zuckerkrankheit Diabetes mellitus. Steatosis is defined as the accumulation of fatty acids in the form of triglycerides in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes. That is the accumulation of fat in the liver is usually small not causing inflammation. Hepatic steatosis is an accumulation of fat in the liver.
2 Initially TAG synthesis and accumulation of fat in the liver are thought to be hepatoprotective. Liver steatosis is graded based on the percentage of fat within the hepatocytes. Bei einer Steatosis hepatis Grad 2 liegt also eine mäßig ausgeprägte Fettleber vor. That is the accumulation of fat in the liver is usually small not causing inflammation. Moreover in most cases we have a mild hepatic steatosis which is medically referred to as grade 1 or 2 hepatic steatoses which usually does not lead to complications or progress to more severe stages or cause symptoms. Hepatic steatosis is becoming the most common cause of chronic liver disease and also contributes to worsening Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The correlation of the degree of HS between CAP and US was significantly high in patients with HS and the optimal cut-off CAP values for grade 2 to 3 and grade 3 HS were 2845 and 2985 dBm.




























Posting Komentar untuk "Steatosis Hepatis Grad 2"