Heat Treatment Process For Steel
Heat treatment process for steel. Heat the steel to 30 50 degrees above Ac3 or Accm after soaking cool it at a cooling rate slightly larger than that of annealing. Improve the toughness Increase the hardness Increase the ductility Improve the machinability Refine the grain structure Remove the residual stresses Improve the wear resistance 4. Carbon steels molecular structure is crystalline.
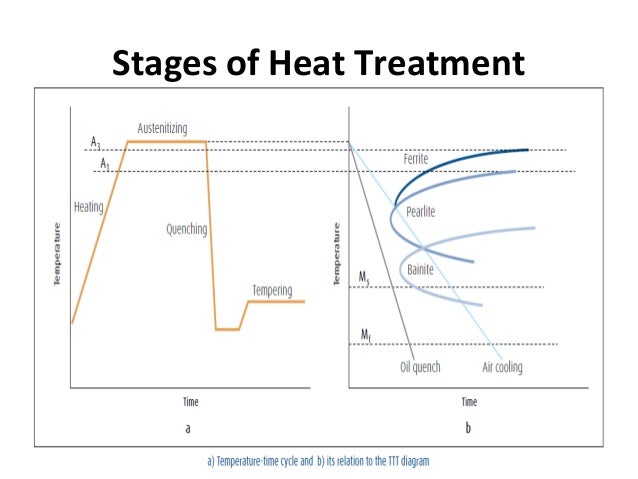
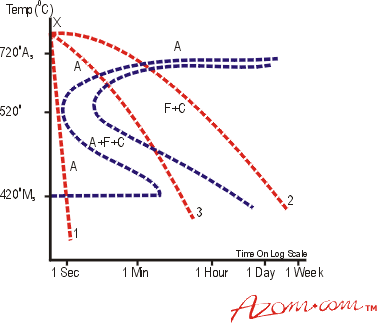
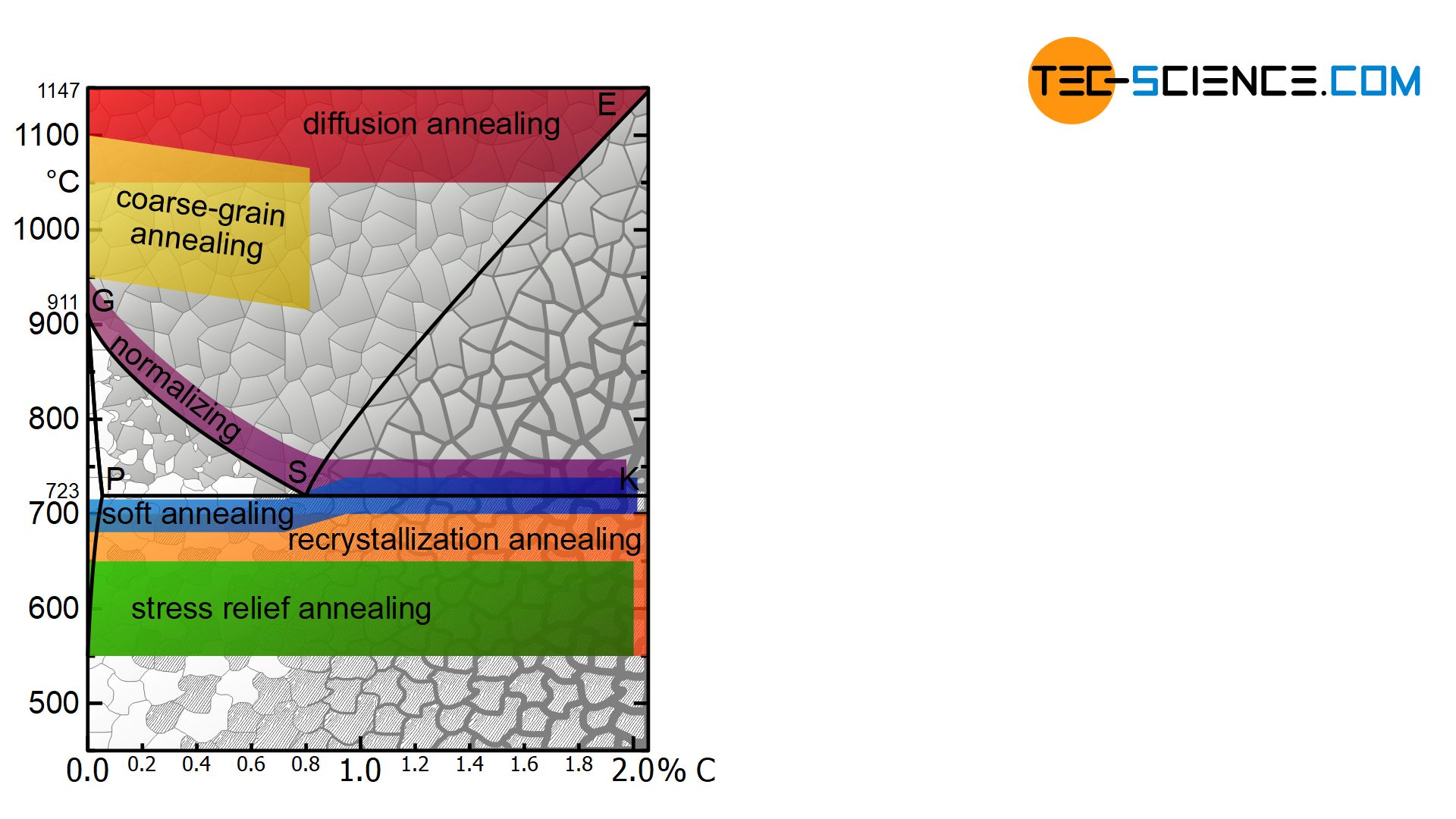
Heat treatment is effective on compositions above the eutectoid composition hypereutectoid of 08 carbon. Isothermal annealing Heat treatment of a steel by austenitizing cooling rapidly to a temperature between the A1 ant the nose of the TTT. Austempering -The isothermal heat treatment by which austenite transforms to bainite.
Second Edition matrix and a new phase is formed which is called austenite. The softening hardening and thermochemical processes are some of the most common heat treatments for steel. Results in considerable coarsening of austenitic grains heavy scale.
General heat treatment procedures are given for annealing normalizing hardening tempering case hardening surface hardening and special treatments such as austempenng ausforming mar- tempering and cold treatment. The Steel parts produced by mechanical operation process such as casting rolling or drawing extruding. As you have read these processes are used for metal material modifications and the behavior of steel to maximize a products service life.
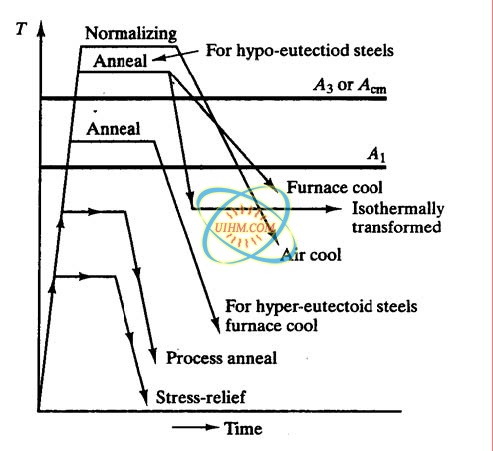
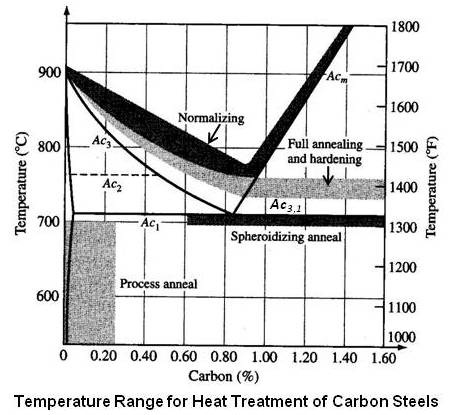
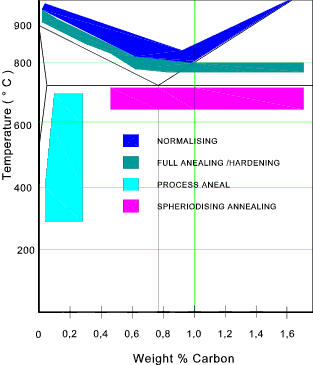
The basic principles involved in the heat treat- ment of these materials are presented in simplified form. Normalizing is a heat treatment process similar to annealing in which the Steel is heated to about 50. In this episode basics and fundamentals of Heat treatment process of Steels are described.
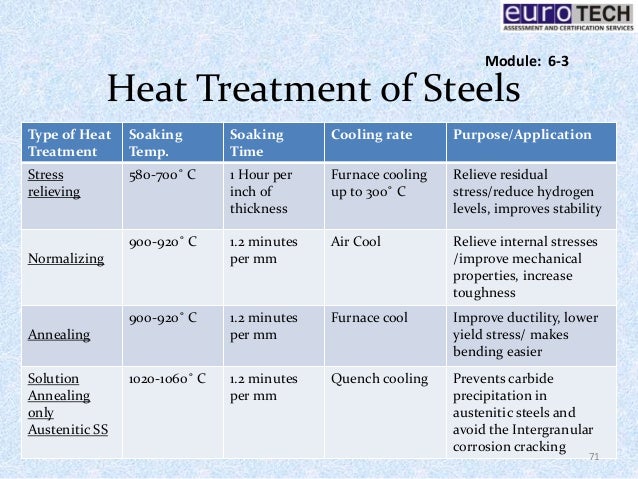
Heat treatment of steel is accomplished by heating it above upper critical temperature Ac3. The normal processes used for the heat treatment of steels are i annealing ii normalizing iii hardening and iv tempering. 10 Practical Heat Treating.
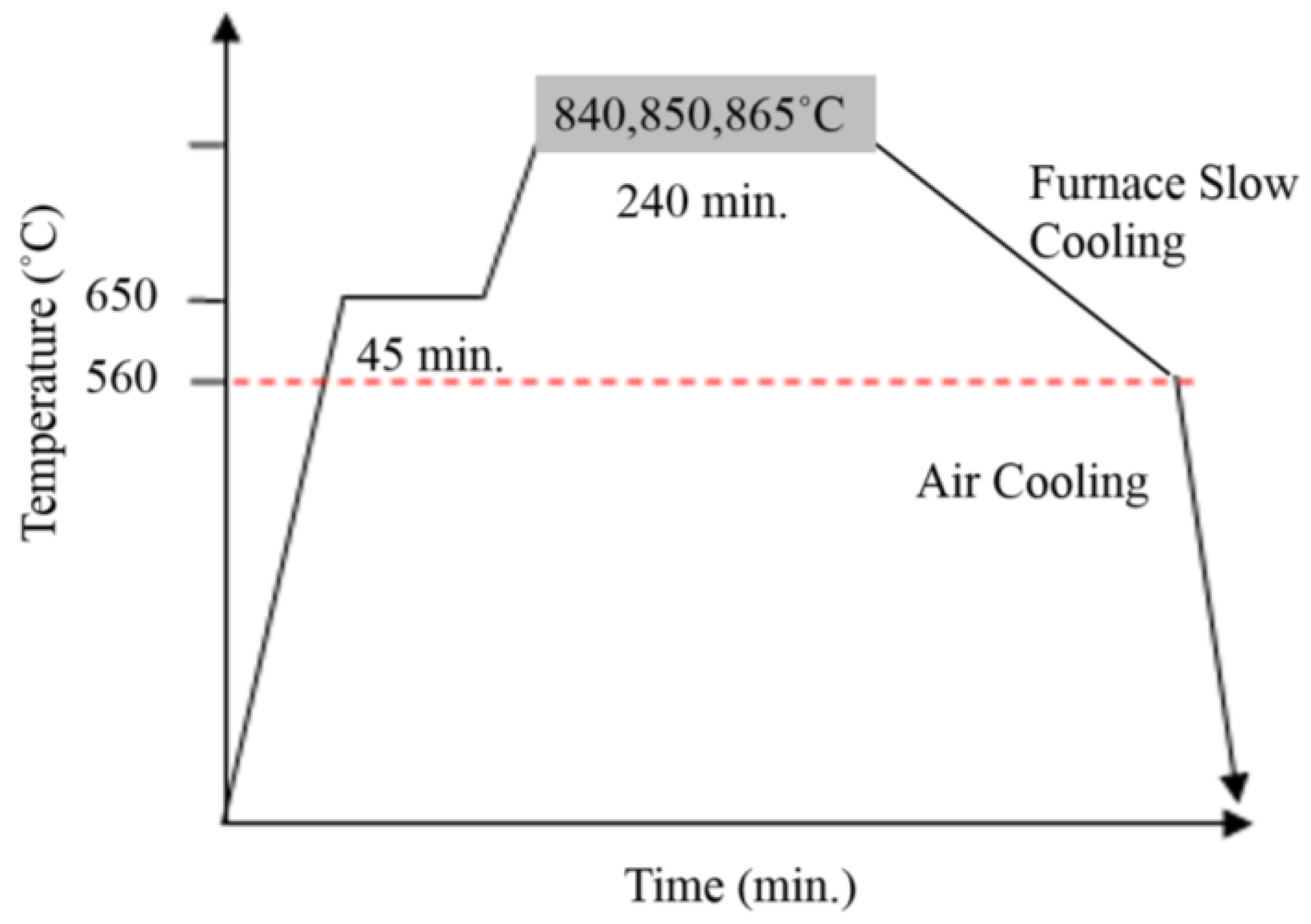
Note that phases of steel should not be confused with structures. Steel is heated sufficiently above the upper critical temperature say 1000-2000o C and held at this temperature for 10-20 hours followed by slow cooling.
Heating to such a high temp.
In this episode basics and fundamentals of Heat treatment process of Steels are described. Note that phases of steel should not be confused with structures. Heating to such a high temp. Various types of heat treatment processes are used to modify the following properties or conditions of the steel. Carburization Carburization is a heat treatment process in which steel or iron is heated to a temperature below the melting point in the presence of a liquid solid or gaseous material which decomposes so as to release carbon when heated to the temperature used. Along with that Introduction to Annealing is also explained. Austempering -The isothermal heat treatment by which austenite transforms to bainite. Results in considerable coarsening of austenitic grains heavy scale. Segregated zones are eliminated and a chemically homogeneous steel is obtained by this treatment as a result of diffusion.
There are only three phases involved in any steelferrite carbide cementite and aus-tenite. Exposure to hot and cool temperatures will change the shape or phase of these crystals. Heat the steel to 30 50 degrees above Ac3 or Accm after soaking cool it at a cooling rate slightly larger than that of annealing. Isothermal annealing Heat treatment of a steel by austenitizing cooling rapidly to a temperature between the A1 ant the nose of the TTT. As you have read these processes are used for metal material modifications and the behavior of steel to maximize a products service life. Heat treatment of steel is accomplished by heating it above upper critical temperature Ac3. Various types of heat treatment processes are used to modify the following properties or conditions of the steel.





























Posting Komentar untuk "Heat Treatment Process For Steel"