Spray Modelling Using Probability
Spray modelling using probability. Soot formation in an n-dodecane spray flame under diesel engine conditions known as Spray A is modelled with the transported probability function TPDF method. The developed model does not rely on any fitting parameters except for the value of the parameter determining the probability of successful wet position collisions which is computed using the MC simulations and then transferred to the population balance modeling part. Two methodologies are used.
Modeling of sub-grid conditional mixing statistics in turbulent sprays using machine learning methods. Stein Conditional scalar dissipation rate modeling for turbulent spray flames using artificial neural networks. An n-dodecane spray Spray A injected into a high-pressure and high-temperature combustion vessel at typical diesel engine conditions is investigated using the transported probability density function TPDF method.
In this chapter a modelling technique for the prediction of spray flame and soot formation has been discussed in connection with the kerosene fuel. A probability density function PDF based approach for modeling spray combustion in the large eddy simulation LES context is used to study a series of experimental spray flames. The approach employs an acetylene-based two-equation soot model coupled with a Reynolds-averaged turbulence model and a Lagrangian discrete phase spray model.
The approach can simulate both dense and dilute regions of the spray. An n-dodecane spray in temperature and pressure conditions typical of diesel engines known as Spray A is modelled by the transported probability density function TPDF method. In the present thesis turbulent spray flows are investigated using probability density function PDF methods.
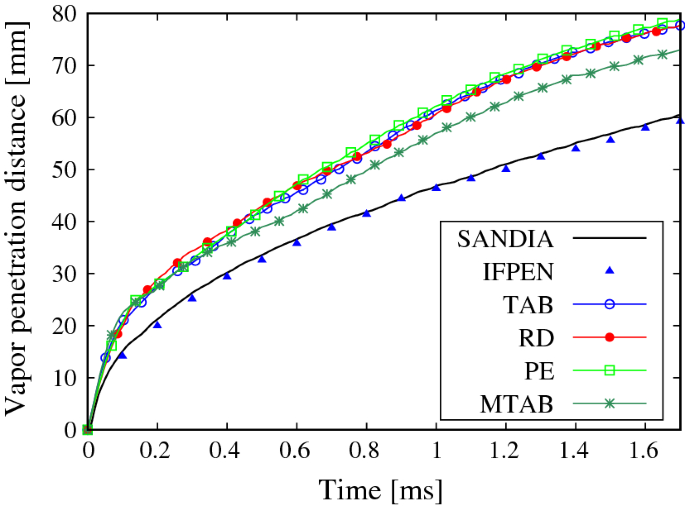
Validation of the implemented secondary breakup model including the spray tip penetration spray angle Sauter mean diameter and droplet distribution. Atomization probability density functions PDF stochastic fields large eddy simulation LES engine combustion network ECN Spray A. Complex coupling of droplet dispersion evaporation and scalar mixing in turbulent spray-laden flows results in a range of combustion regimes.
The MEPDF approach together with the conserved scalar formulation and the real-fluid library is utilized to account for the scalar. Possible outcomes would include 123456 and their corresponding probabilities would be 101520151030. This paper presents a numerical modeling study of one ethanol spray flame from the Delft Spray-in-Hot-Coflow DSHC database which has been used to study Moderate or Intense Low-oxygen Dilution MILD combustion of liquid fuels Correia Rodrigues et.
Considering the computational economy we have restricted the discussion on RANS-based modelling which is still popular in the industrial scale for the prediction of combustion phenomenon. Fluids 1 541 1958 are establishedThe equation governing the ddf evolution is derived using an alternative approach.
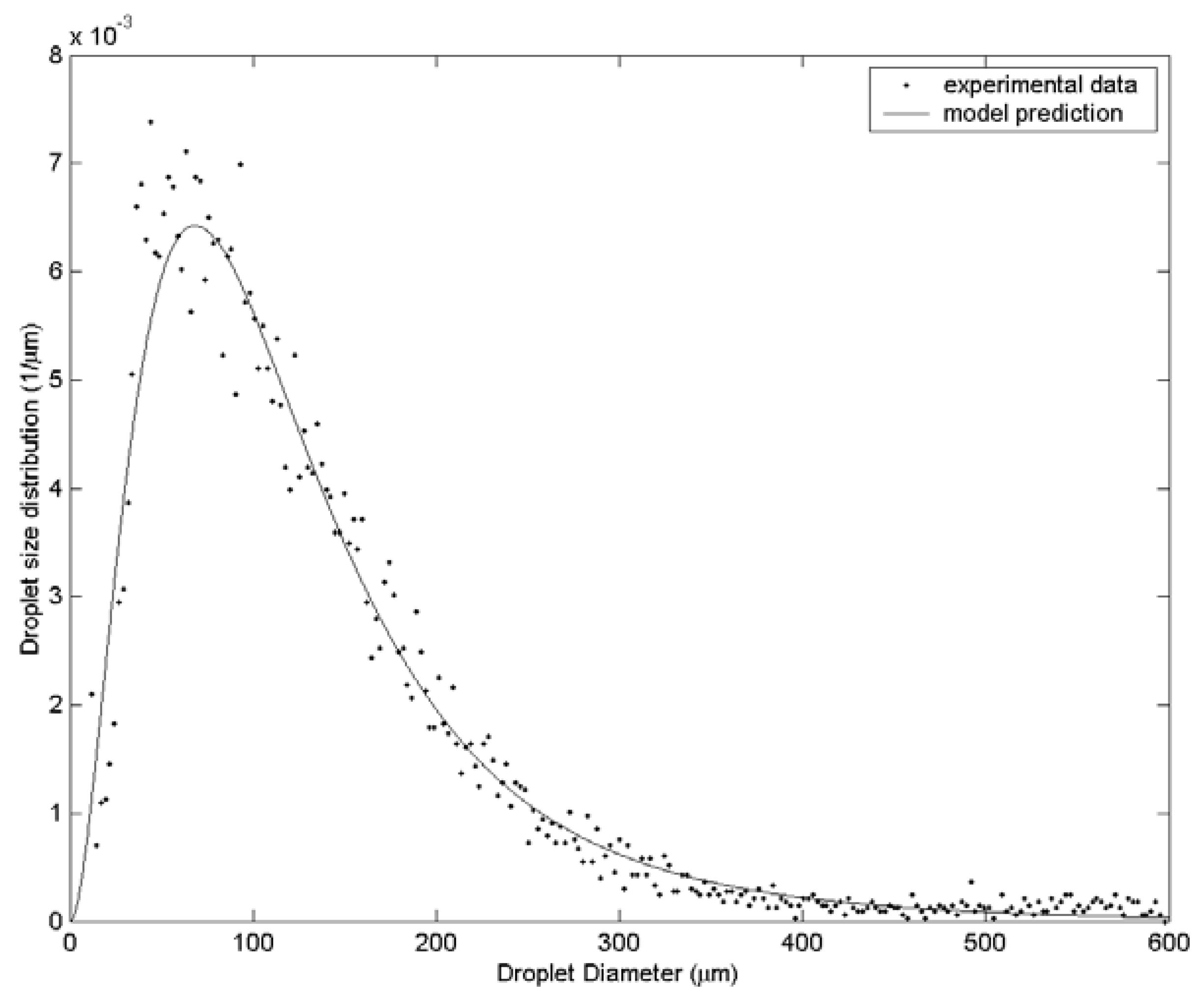
At the same time use of the probability density function brings additional information regarding drop size distribution.
In the present thesis turbulent spray flows are investigated using probability density function PDF methods. Validation of the implemented secondary breakup model including the spray tip penetration spray angle Sauter mean diameter and droplet distribution. Sauter mean diameter is predicted well using our formulation. In the present chapter a one-point one-time Eulerian statistical description of a joint mixture fractionenthalpy probability density function pdf model for the gas phase is derived and modeled. Fluids 1 541 1958 are establishedThe equation governing the ddf evolution is derived using an alternative approach. The approach adopted is based on the evolution equation for the joint probability density function PDF of the droplet properties. A probability density function PDF based approach for modeling spray combustion in the large eddy simulation LES context is used to study a series of experimental spray flames. Now what if instead my new game at the casino was to roll a fixed die. An n-dodecane spray in temperature and pressure conditions typical of diesel engines known as Spray A is modelled by the transported probability density function TPDF method coupled with a time-dependent Reynolds-averaged k turbulence model and a Lagrangian discrete phase model of the liquid spray.
Atomization probability density functions PDF stochastic fields large eddy simulation LES engine combustion network ECN Spray A. The theoretical foundations of a statistical spray modeling approach based on the droplet distribution function ddf which was originally proposed by Williams Phys. At the same time use of the probability density function brings additional information regarding drop size distribution. Two methodologies are used. The developed model does not rely on any fitting parameters except for the value of the parameter determining the probability of successful wet position collisions which is computed using the MC simulations and then transferred to the population balance modeling part. The method consist of solving a joint sub-grid probability density function of liquid volume and surface using stochastic methods. EulerianLagrangian spray atomisation with adaptive mesh refinement and a stochastic fields transported probability density function method.


























Posting Komentar untuk "Spray Modelling Using Probability"